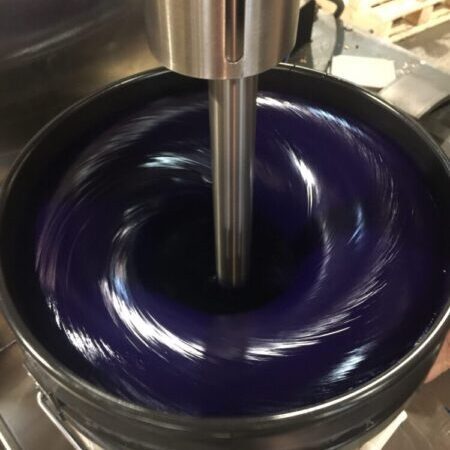
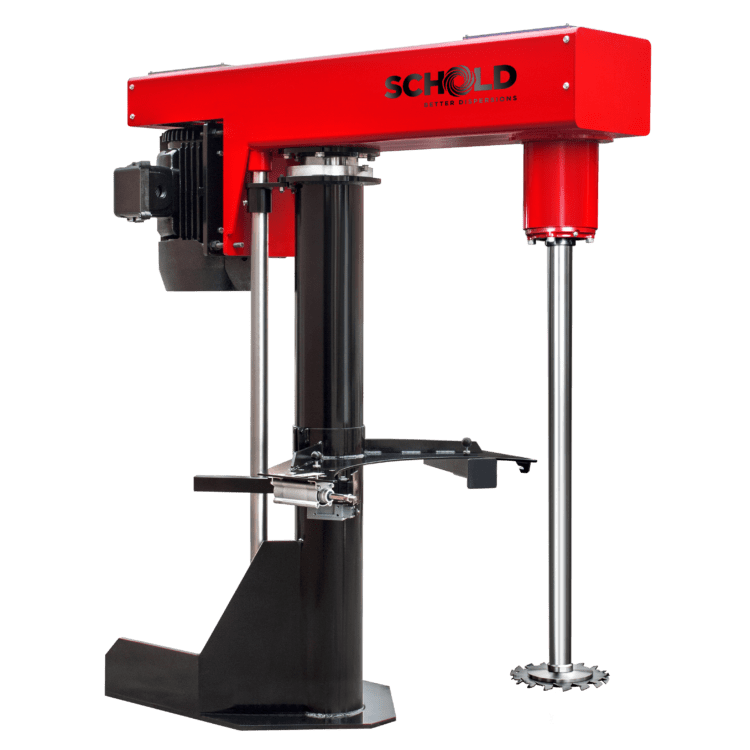
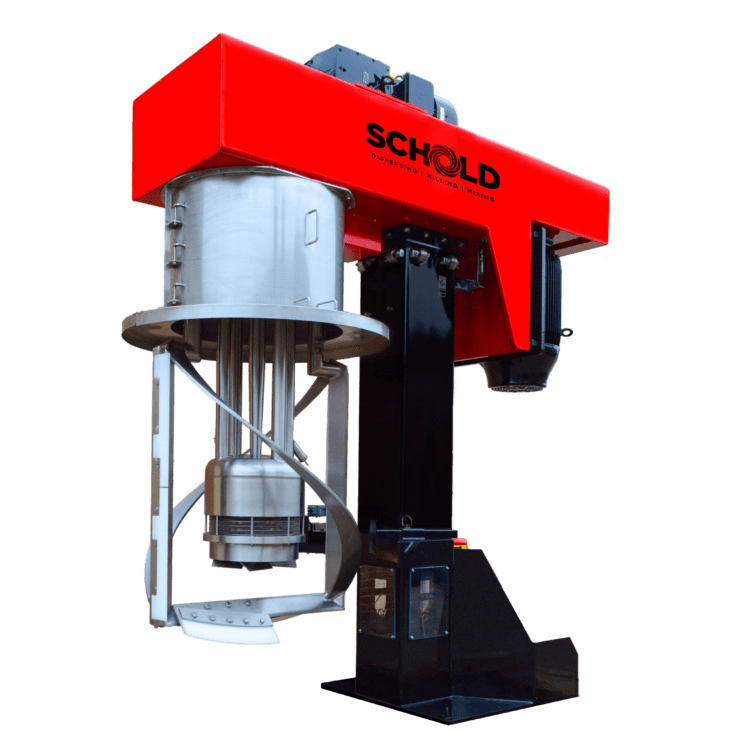
Mixing Equipment for Paints Inks and Coatings
Mixing Equipment for Paints Inks and Coatings
Recommended Mixing Equipment
TRUSTED COMPANIES USING SCHOLD MIXING EQUIPMENT FOR PAINTS, INKS, AND COATINGS:






Schold Customer Spotlights

Handy Art
Handy Art has been a trusted Schold partner since the early 1980s, manufacturing water based paints, inks, and glues. They have expanded dramatically over the years and Schold has been there every step of the way as their exclusive mixing equipment partner.
“We chose Schold because of the robustness of their equipment, but the service and high ethics are a bonus. We don’t have a maintenance department, so the the durability of Schold’s mixing equipment is essential for our success. Schold has been a great partner and we now have 6 mixers, all original, that date from the early 80’s!”
-Ansel Jackson, COO

Kerley Ink
Long-time customer Kerley Ink is known for its major contributions to the ink printing industry. We met with President John Whalen to add mixing equipment robust enough to tackle the resin bases derived from tree sap, which is famously used in the Kerley product.
“We are almost entirely a Schold house with little exception. The Schold retrofitting services have been very successful, and the VFD technology is so quiet, you can have a conversation next to the machine at full power. Our oldest machine is from the Kennedy era… it’s been running strong ever since I was five years old!”
-John Whalen, President
Product Applications



- Pigment Dispersion: Achieving uniform dispersion of pigments in liquid mediums to produce vibrant and consistent colors in paints, inks, and coatings.
- Ink Production: Blending and dispersing colorants, binders, and other additives to formulate inks used in printing processes such as offset, gravure, and flexographic printing.
- Paint Formulation: Creating paint formulations by dispersing pigments, resins, solvents, and additives to achieve desired color, consistency, and performance properties.
- Coating Development: Formulating coatings for diverse applications, including automotive coatings, architectural coatings, and industrial coatings, by dispersing and blending various components.
- Emulsion Polymerization: Dispersing monomers and initiating polymerization to produce polymer emulsions used in water-based paints, coatings, and inks.
- Inkjet Ink Manufacturing: Precisely dispersing colorants and additives for the production of inks used in inkjet printing technologies.
- Adhesive Coatings: Formulating coatings for adhesives used in industries such as packaging and construction, involving the dispersion of adhesive components.
- UV-Curable Inks and Coatings: Formulating inks and coatings that cure rapidly under ultraviolet (UV) light, requiring precise mixing and dispersion of photo initiators and reactive monomers.
- High-Performance Coatings: Developing specialty coatings with specific properties such as corrosion resistance, chemical resistance, or high durability through controlled dispersion of additives.
- Automotive Paints: Preparing automotive paints with precise color matching and dispersion of pigments, metallic flakes, and other components.
- Anti-Corrosion Coatings: Creating coatings designed to prevent corrosion on metal surfaces through the dispersion of corrosion inhibitors and protective additives.
- Industrial Inks: Formulating inks used in industrial printing applications, such as coding and marking, by blending colorants and other functional additives.
- Wood Coatings: Formulating coatings for wood surfaces, including stains, varnishes, and protective coatings, by dispersing components to achieve desired aesthetics and performance.
- Cosmetic Inks and Coatings: Preparing inks and coatings for cosmetic applications, including makeup and personal care products, through controlled dispersion of pigments and additives.
- Textile Printing Inks: Formulating inks for textile printing, involving the dispersion of colorants and other additives to achieve desired print quality and durability.
- Specialty Coatings for Electronics: Developing coatings for electronic components, such as conformal coatings, through precise dispersion of materials for protection and insulation.
- Pigment Dispersion: Achieving uniform dispersion of pigments in liquid mediums to produce vibrant and consistent colors in paints, inks, and coatings.
- Ink Production: Blending and dispersing colorants, binders, and other additives to formulate inks used in printing processes such as offset, gravure, and flexographic printing.
- Paint Formulation: Creating paint formulations by dispersing pigments, resins, solvents, and additives to achieve desired color, consistency, and performance properties.
- Coating Development: Formulating coatings for diverse applications, including automotive coatings, architectural coatings, and industrial coatings, by dispersing and blending various components.
- Emulsion Polymerization: Dispersing monomers and initiating polymerization to produce polymer emulsions used in water-based paints, coatings, and inks.
- Inkjet Ink Manufacturing: Precisely dispersing colorants and additives for the production of inks used in inkjet printing technologies.
- Adhesive Coatings: Formulating coatings for adhesives used in industries such as packaging and construction, involving the dispersion of adhesive components.
- UV-Curable Inks and Coatings: Formulating inks and coatings that cure rapidly under ultraviolet (UV) light, requiring precise mixing and dispersion of photoinitiators and reactive monomers.
- High-Performance Coatings: Developing specialty coatings with specific properties such as corrosion resistance, chemical resistance, or high durability through controlled dispersion of additives.
- Automotive Paints: Preparing automotive paints with precise color matching and dispersion of pigments, metallic flakes, and other components.
- Anti-Corrosion Coatings: Creating coatings designed to prevent corrosion on metal surfaces through the dispersion of corrosion inhibitors and protective additives.
- Industrial Inks: Formulating inks used in industrial printing applications, such as coding and marking, by blending colorants and other functional additives.
- Wood Coatings: Formulating coatings for wood surfaces, including stains, varnishes, and protective coatings, by dispersing components to achieve desired aesthetics and performance.
- Cosmetic Inks and Coatings: Preparing inks and coatings for cosmetic applications, including makeup and personal care products, through controlled dispersion of pigments and additives.
- Textile Printing Inks: Formulating inks for textile printing, involving the dispersion of colorants and other additives to achieve desired print quality and durability.
- Specialty Coatings for Electronics: Developing coatings for electronic components, such as conformal coatings, through precise dispersion of materials for protection and insulation.
Mixing/Processing Challenges
- Pigment Dispersion and Color Matching: Achieving consistent and thorough dispersion of pigments to ensure uniform coloration and prevent color variations in paints, inks, and coatings. (See VHS High-Speed Disperser)
- Particle Size Control: Maintaining precise control over particle size distribution during milling processes to achieve the desired texture, finish, and performance properties in the final product. (See Media/Bead Mills)
- Viscosity Management: Managing variations in viscosity, especially in formulations with high-solid content, to maintain proper flow characteristics during processing with dispersers and mixers. (See VLS Low-Speed Mixer or Multi-Shaft Mixer)
- Thixotropic Behavior: Controlling thixotropic behavior, where the material becomes less viscous under shear, to ensure proper application and prevent issues like sagging or uneven coverage.
- Degassing: Effectively managing and removing entrapped air and gases during the processing stages to prevent voids, bubbles, and surface defects in the final product.
- Reactive Formulations: Managing the challenges associated with reactive formulations, including two-part coatings or inks, to achieve proper mixing and avoid premature curing.
- Temperature Sensitivity: Addressing the impact of temperature on sensitive materials, such as resins and binders, during processing to ensure stability and performance. (See VDM Vacuum Drum Mixer)
- Abrasive Wear on Equipment: Addressing wear and tear on milling and mixing equipment due to abrasive materials, ensuring equipment durability and consistent performance over time.
- Scale-Up Challenges: Adapting laboratory-scale processes to larger industrial scales while maintaining precision, consistency, and efficiency in material dispersion and blending.
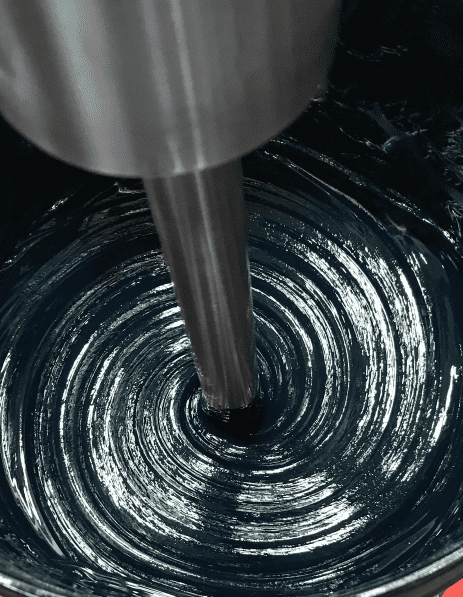
- Pigment Dispersion and Color Matching: Achieving consistent and thorough dispersion of pigments to ensure uniform coloration and prevent color variations in paints, inks, and coatings. (See VHS High-Speed Disperser)
- Particle Size Control: Maintaining precise control over particle size distribution during milling processes to achieve the desired texture, finish, and performance properties in the final product. (See Media/Bead Mills)
- Viscosity Management: Managing variations in viscosity, especially in formulations with high-solid content, to maintain proper flow characteristics during processing with dispersers and mixers. (See VLS Low-Speed Mixer or Multi-Shaft Mixer)
- Thixotropic Behavior: Controlling thixotropic behavior, where the material becomes less viscous under shear, to ensure proper application and prevent issues like sagging or uneven coverage.
- Degassing: Effectively managing and removing entrapped air and gases during the processing stages to prevent voids, bubbles, and surface defects in the final product.
- Reactive Formulations: Managing the challenges associated with reactive formulations, including two-part coatings or inks, to achieve proper mixing and avoid premature curing.
- Temperature Sensitivity: Addressing the impact of temperature on sensitive materials, such as resins and binders, during processing to ensure stability and performance. (See VDM Vacuum Drum Mixer)
- Abrasive Wear on Equipment: Addressing wear and tear on milling and mixing equipment due to abrasive materials, ensuring equipment durability and consistent performance over time.
- Scale-Up Challenges: Adapting laboratory-scale processes to larger industrial scales while maintaining precision, consistency, and efficiency in material dispersion and blending.






